Mastering Human Heart Drawing: Your Guide To Anatomical Artistry
Have you ever found yourself captivated by the intricate beauty of the human body, specifically its most vital organ, the heart? Perhaps you're an aspiring artist, a curious student of anatomy, or simply someone looking for a new creative challenge. Whatever your motivation, learning the art of human heart drawing is a fascinating journey that combines artistic skill with a deeper understanding of biology. It's an endeavor that's often perceived as complex, but with the right guidance, it's far more accessible than you might imagine.
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the process, offering a step-by-step approach to drawing a realistic and anatomically accurate human heart. We'll explore everything from the foundational knowledge of cardiac anatomy to the essential tools and techniques that will bring your artwork to life. Whether you're a complete beginner or looking to refine your existing skills, prepare to get to the heart of the matter and discover how simple it truly is to depict this incredible organ on paper.
Table of Contents
- Why Draw the Human Heart? More Than Just Art
- Understanding the Anatomy Before You Draw
- Essential Tools for Your Human Heart Drawing
- Step-by-Step Approach to Drawing a Human Heart
- Beyond the Basics: Advanced Techniques for Realism
- Learning Resources and Inspiration for Your Heart Drawing
- Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them in Heart Drawing
- Applying Your Skills: More Than Just Anatomy
Why Draw the Human Heart? More Than Just Art
The act of drawing, particularly something as complex and vital as the human heart, offers a multitude of benefits beyond merely creating an image. For many, it's a deep dive into anatomy, a way to truly understand the intricacies of this incredible organ. When you engage in a human heart drawing, you're not just sketching lines; you're actively learning about its structure, its chambers, and the major vessels that connect to it. This hands-on approach to learning can solidify anatomical knowledge in a way that simply reading a textbook cannot. It’s an immersive experience that transforms abstract concepts into tangible forms.
Beyond the educational aspect, drawing the heart can be a profoundly meditative and rewarding experience. It hones your observation skills, your precision, and your ability to translate three-dimensional forms onto a two-dimensional surface. For beginners, it builds foundational drawing skills such as understanding basic shapes, proportions, and shading. For more experienced artists, it presents a challenge to capture the nuances of texture, depth, and the organic flow of biological forms. Furthermore, there's a unique satisfaction in depicting something so essential to life, making your artwork not just visually appealing but also imbued with a sense of purpose and meaning. This is why a human heart drawing holds such a special place in anatomical illustration and artistic expression.
Understanding the Anatomy Before You Draw
To truly capture the essence of the human heart in your drawing, a foundational understanding of its anatomy is indispensable. You don't need to be a cardiologist, but knowing the basic structure and function will elevate your artwork from a mere sketch to an anatomically informed illustration. This knowledge is crucial for adhering to the E-E-A-T principles, ensuring your drawing is not only aesthetically pleasing but also accurate and trustworthy. Remember, the heart is a vital organ that functions as a pump, providing blood throughout your body. Its complex design is a marvel of natural engineering, and understanding it will guide your artistic choices.
The Heart's Basic Structure and Function
The human heart is roughly the size of a clenched fist and is located slightly to the left of the center of your chest, behind and slightly to the left of your breastbone. Its base is located along the body's midline with the apex pointing toward the left side. Because the heart points to the left, about two-thirds of the heart's mass is found on the left side of the body. This orientation is key to accurately positioning your human heart drawing.
Internally, the heart is divided into four chambers: two upper atria and two lower ventricles. These chambers work in a coordinated fashion to pump blood. The right side of the heart receives deoxygenated blood from the body and pumps it to the lungs, while the left side receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it out to the rest of the body. When you look at a medical diagram of an anatomical heart drawing, you'll often see blue sections representing deoxygenated blood and red sections representing oxygenated blood. Incorporating this color distinction, even subtly, can add a layer of anatomical correctness to your artwork.
Key Vessels: Aorta and Pulmonary Arteries
Crucial to the heart's function are the major blood vessels connected to it. The largest artery in the body, the aorta, emerges from the top of the left ventricle and arches over the heart, distributing oxygenated blood to the entire body. When drawing the heart, the aorta is one of the most prominent features and often serves as a central anchor for other structures. We will be drawing the main part facilitating these pipes, called the aorta, in this tutorial.
Other important vessels include the pulmonary arteries (carrying deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs) and pulmonary veins (carrying oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium), as well as the superior and inferior vena cava (bringing deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium). Understanding the relative positions and sizes of these vessels is paramount for creating a realistic human heart drawing. Referencing a good diagram, perhaps from an old nurse's anatomy book or a reliable online source, is highly recommended to ensure accuracy in your depiction of the internal structure and external connections.
Essential Tools for Your Human Heart Drawing
Before you embark on your artistic journey of creating a human heart drawing, gathering the right tools is a simple yet crucial step. You don't need an elaborate art studio; a few basic items will suffice to get started. The quality of your tools can influence the ease and outcome of your drawing, so choose wisely, even if you're a beginner.
- Pencil: A standard graphite pencil (HB or 2B is a good starting point) is essential for sketching your initial outlines. Its erasability allows for corrections and refinements as you develop your drawing.
- Black Pen: Once your sketch is finalized, a black pen (fine-liner or gel pen) is perfect for inking your lines, making them crisp and permanent. This step adds definition and professionalism to your human heart drawing.
- Eraser: A good quality eraser is indispensable. It allows you to clean up guide lines, correct mistakes, and even create highlights by lifting graphite.
- Paper: Choose drawing paper that is smooth enough for fine details but has enough tooth to hold graphite or ink. Standard sketch paper or even good quality printer paper can work for practice.
- Reference Images: While not a physical tool, having a clear anatomical diagram or a detailed illustration of a human heart is paramount. This will serve as your guide for accuracy, especially when depicting the internal structure.
With these simple tools in hand, you're well-equipped to start your human heart drawing journey. Remember, the goal is not perfection on your first try, but rather to enjoy the process of learning and creating.
Step-by-Step Approach to Drawing a Human Heart
Drawing a human heart is easier than you may think, especially when broken down into manageable steps. This section will guide you through the process, from initial outlines to adding intricate details, ensuring your human heart drawing is both accurate and visually appealing. Follow these simple steps, and you too can easily draw a realistic heart.
Starting with Simple Shapes and Outlines
Every complex drawing begins with simple shapes. For a human heart drawing, think of it as a slightly irregular pear or an inverted teardrop shape. Start by lightly sketching a basic oval or rounded shape that will form the main mass of the heart. This initial shape doesn't need to be perfect; it's just a guide for proportion and placement on your paper.
- Establish the Apex and Base: The apex (the pointed bottom) of the heart typically points towards the lower left, while the base (the broader top) is where the major vessels emerge. Lightly mark these points to define the heart's orientation.
- Divide into Chambers (Roughly): Mentally or lightly sketch a vertical line down the center to represent the septum, dividing the heart into left and right halves. Then, a horizontal line can roughly separate the atria from the ventricles. These are purely compositional guides at this stage.
- Outline the Major Vessels: Now, start sketching the large vessels emerging from the top. The aorta, being the largest, will be prominent. Sketch its curved path as it arches over the heart. Add the pulmonary artery next to it, typically anterior to the aorta. Also, indicate where the vena cava and pulmonary veins would connect. These initial lines are the framework for your detailed human heart drawing.
Keep your lines light and loose in this stage. This allows for easy corrections and adjustments as you refine the overall form. Think of it as building a skeleton before adding the muscles and skin.
Adding Details, Shading, and Color
Once your basic outline is established, it's time to bring your human heart drawing to life with details, shading, and potentially color. This is where the intricacies and details of this vital organ truly begin to emerge.
- Refine the Contours: Go over your initial light lines with more confident strokes, shaping the curves and undulations of the heart's surface. Pay attention to the coronary arteries and veins that run along the surface; these add a layer of realism.
- Internal Structures (Optional but Recommended): If you're aiming for an anatomically correct human heart drawing, you'll want to depict the internal structure. Refer to a good diagram to illustrate the four chambers, the valves (like the mitral and tricuspid valves), and the septum. This requires precision and a good understanding of spatial relationships within the heart.
- Shading for Depth: Shading is crucial for giving your drawing a three-dimensional quality. Identify your light source and apply darker tones to areas that would be in shadow, such as the crevices between chambers or beneath vessels. Use cross-hatching, stippling, or smooth blending techniques to create varying degrees of darkness. This adds volume and realism to your human heart drawing.
- Adding Color: For a full-color heart illustration, remember the convention of using blue for deoxygenated areas (right side of the heart, pulmonary arteries) and red for oxygenated areas (left side of the heart, aorta, pulmonary veins). This color coding not only makes the drawing visually striking but also serves an educational purpose.
- Clean Up: Once you're satisfied with your lines and shading, use your eraser to carefully remove any remaining guide lines or smudges.
By following these steps, you can create a detailed and accurate human heart drawing that showcases both your artistic skill and your understanding of anatomy. The key is patience and continuous refinement.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Techniques for Realism
Once you've mastered the foundational steps of creating a human heart drawing, you might find yourself eager to push the boundaries and achieve an even greater level of realism. Bringing the complexity of a human heart to life through drawing requires a unique blend of technical skill and artistic sensibility. These advanced techniques can help you capture the intricacies and details of this vital organ in your artwork.
- Textural Detail: The heart's surface isn't perfectly smooth. There are muscle fibers, fatty deposits, and the subtle textures of the vessels. Experiment with fine lines, stippling, or subtle cross-hatching to mimic these textures. Observing high-resolution anatomical images will be invaluable here.
- Vascular Networks: Beyond the major arteries and veins, the heart itself is supplied by a network of coronary vessels. Depicting these smaller, branching structures with precision adds immense realism. Pay attention to how they wrap around the heart's surface and dive into its musculature.
- Depth and Form Through Advanced Shading: Move beyond basic light and shadow to explore form more deeply. Use subtle gradients and transitions to show the curvature of the heart's chambers and the roundness of the vessels. Consider reflected light and ambient occlusion to make your human heart drawing pop off the page.
- Color Blending and Layering: If working with color, layer different hues to create rich, vibrant, and realistic tones. For instance, a deep red might be built up with layers of crimson, maroon, and even hints of purple or brown in the shadows, while blue areas can incorporate shades of teal or indigo.
- Perspective and Foreshortening: If you're drawing the heart from a specific angle, understanding perspective and foreshortening will be crucial. This allows you to accurately represent how parts of the heart appear shorter or compressed when viewed head-on, adding dynamic realism to your human heart drawing.
These techniques require practice and patience, but they will undoubtedly take your anatomical illustrations to the next level, showcasing a truly expert understanding of both art and anatomy.
Learning Resources and Inspiration for Your Heart Drawing
In today's digital age, a wealth of resources is available to help you learn and perfect your human heart drawing skills. Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned artist, leveraging these tools can significantly enhance your learning curve and provide endless inspiration.
- Video Tutorials: "Hi everyone, in this video I show you how to draw a human heart step by step, Follow my step by step drawing tutorial and make your own human heart drawing easy!" Many artists and educators offer detailed video tutorials that walk you through the process in real-time. Searching for "how to draw a human heart step by step" on platforms like YouTube will yield numerous helpful guides. These visual aids are excellent for understanding the flow of strokes and the layering of details.
- Free Printable Pages: "Learn how to draw a great looking human heart with easy drawing instructions and video tutorial, plus free printable pages." Many websites offer free printable pages, including outlines and coloring pages, which can serve as excellent practice sheets or templates for beginners. These can help you get a feel for the shape and proportions before attempting a freehand drawing.
- Anatomical Diagrams and Illustrations: "To find a good diagram, go to..." and "Above is a medical diagram of an anatomical heart drawing from an old nurses anatomy book. It is a full color heart illustration with blue and red sections." These are invaluable for accuracy. Look for diagrams that clearly label chambers, valves, and major vessels. Medical textbooks, reputable online anatomy resources, and even historical medical illustrations can provide detailed and accurate references.
- Online Image Databases: "Free download 63 best quality human heart drawing at getdrawings. Search images from huge database containing over 1,250,000 drawings." Websites like GetDrawings.com or Pinterest are fantastic for finding a wide variety of human heart drawing illustrations. You can find different styles, levels of detail, and perspectives to inspire your own work. "Find and save ideas about human heart drawing on Pinterest."
- Artistic Communities: Engaging with online art communities can provide feedback, encouragement, and new techniques. Seeing how other artists approach a human heart drawing can spark new ideas and refine your own methods.
By utilizing these resources, you can continuously learn, refine your techniques, and find endless inspiration for your human heart drawing endeavors.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them in Heart Drawing
While drawing a human heart can be a rewarding experience, there are a few common mistakes that beginners often make. Being aware of these pitfalls can help you avoid them and produce a more accurate and satisfying human heart drawing from the outset.
- Anatomical Inaccuracies: The most common mistake is drawing a heart that looks more like a stylized Valentine's heart than an anatomical one. This often stems from a lack of reference or understanding of the actual organ's shape and proportions.
- Solution: Always use reliable anatomical diagrams as your primary reference. Pay attention to the heart's orientation (apex pointing left), the relative sizes
- Krispy Pizza
- Egg Custard Pie
- American Prohibition Museum
- Donald Trumps Family Circle Will Look Different This Time
- North Harbor Tower
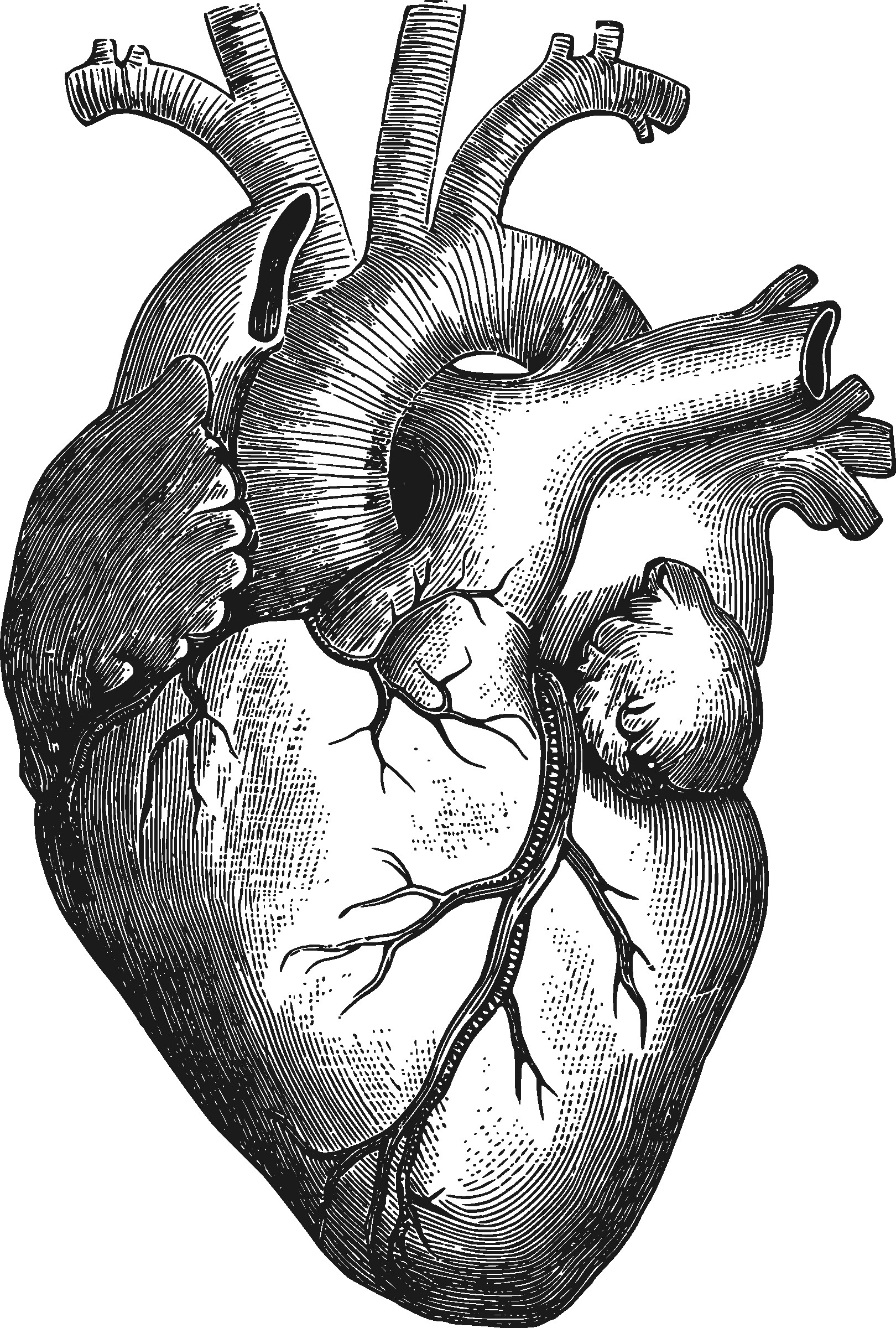
Human Heart Drawing Images at PaintingValley.com | Explore collection

Human Heart Sketches Drawings
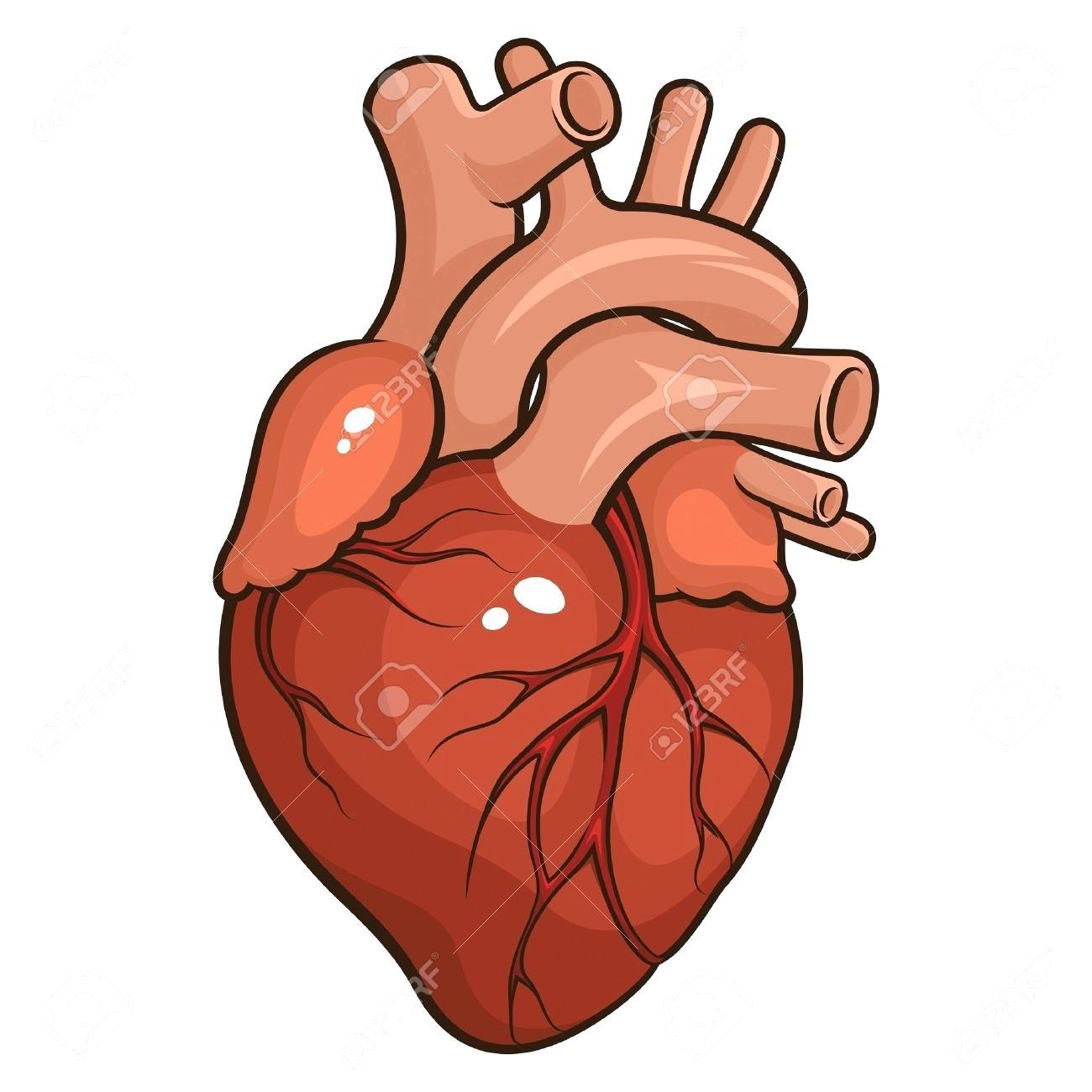
Human Heart Drawing Simple at PaintingValley.com | Explore collection